Configuring the DHCP failover in your LAN is a simple operation to improve the reliability of the network.
There are two main ways to provide DHCP failover:
- Load balancing
- Hot standby
Load balancing allows to share the load between two or more DHCP servers while the Hot standby mode simply provide DHCP redundancy.
In this guide we adopted the Hot standby mode. The DHCP servers are two Windows 2012 R2 machine in the same domain (mandatory requirement).
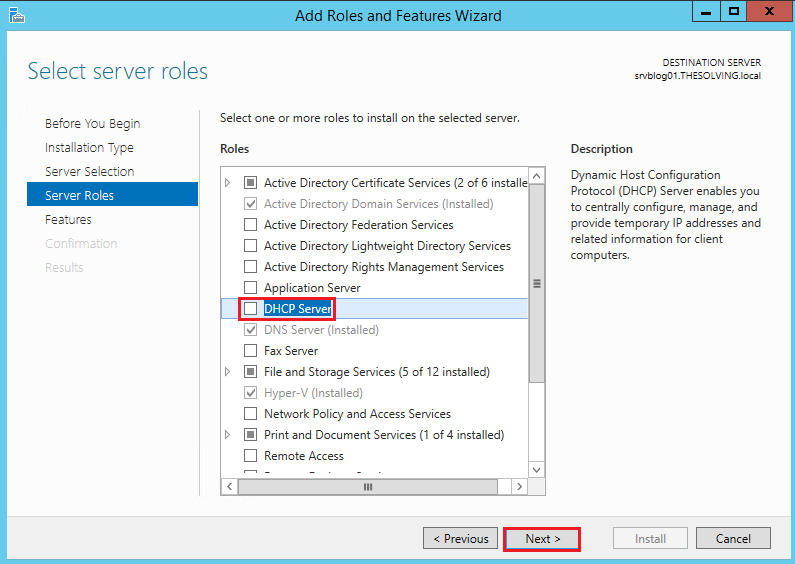
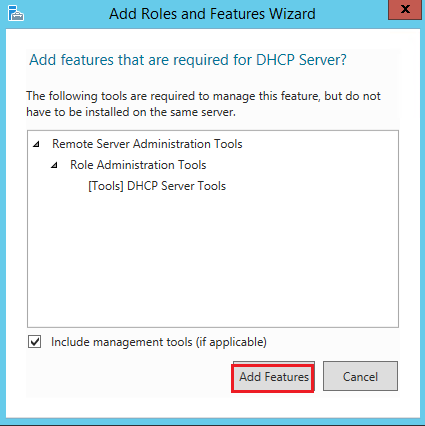
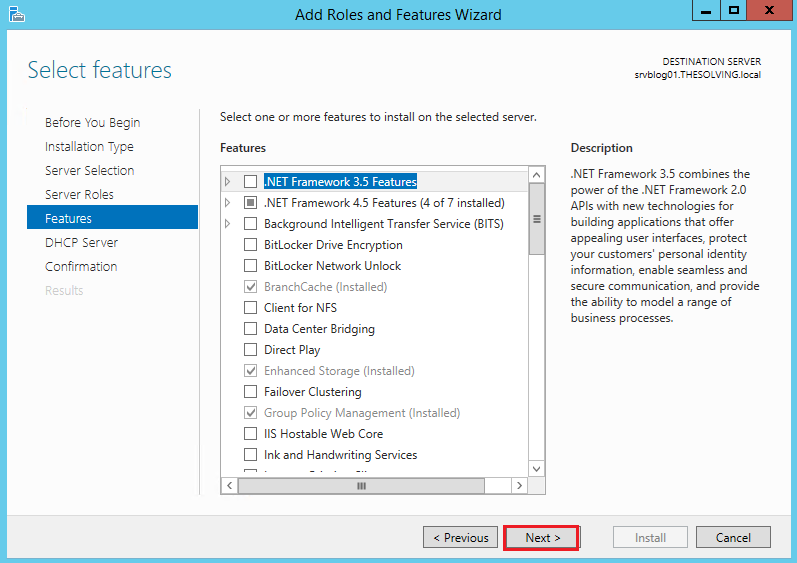
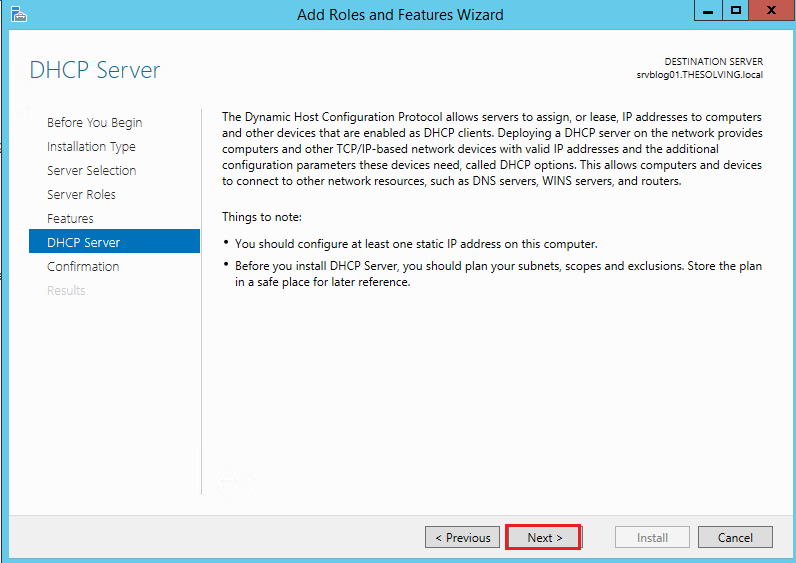
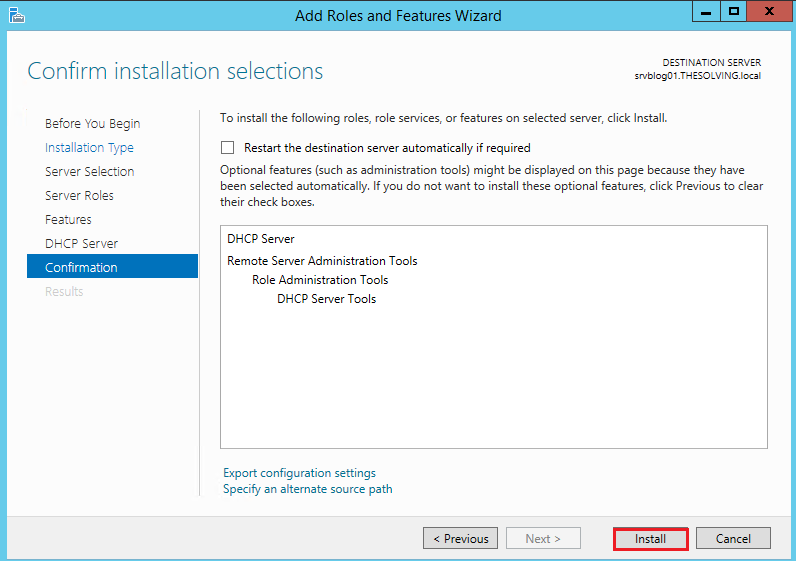
The first step is to install the DHCP server role:
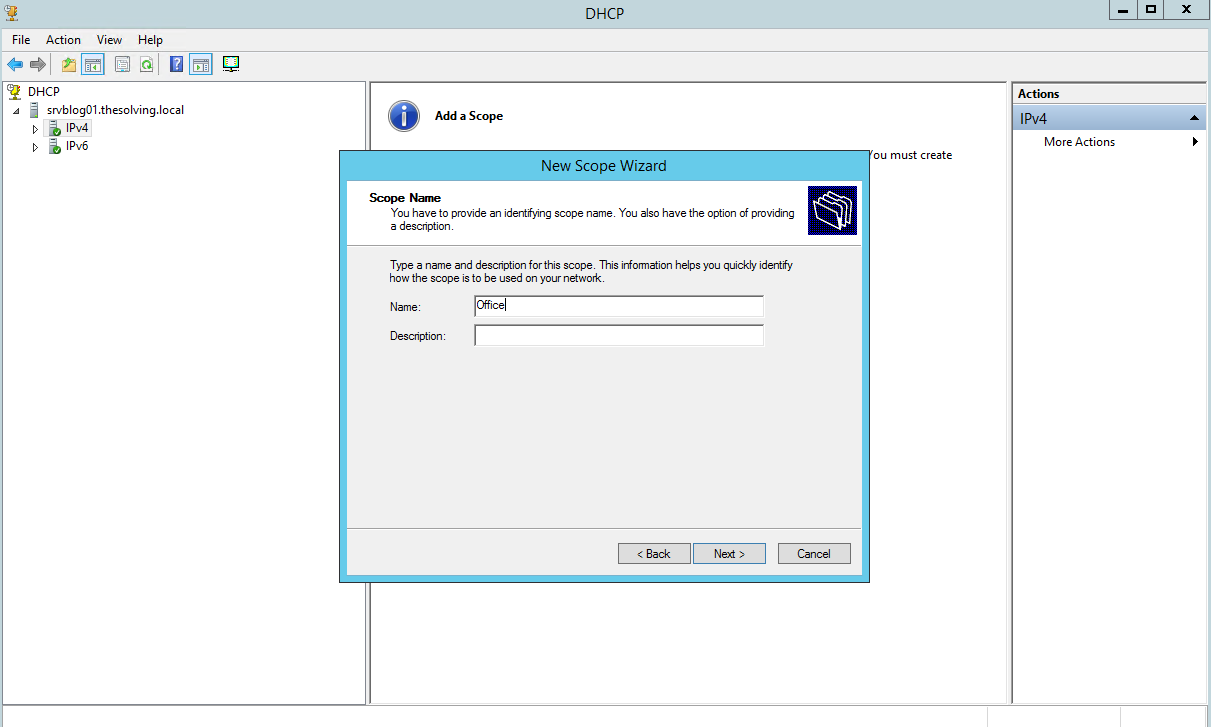
Right-click on IPv4 from the left column and select New Scope, then name it:
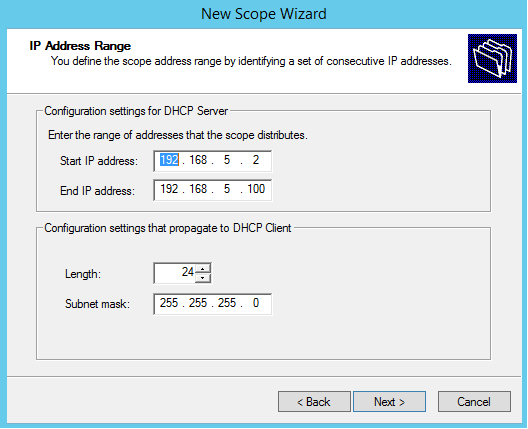
Specify the range of IP addresses that will be assigned by the scope. Note, we are configuring a scope for the Office network (IP range 192.168.5.xyz):
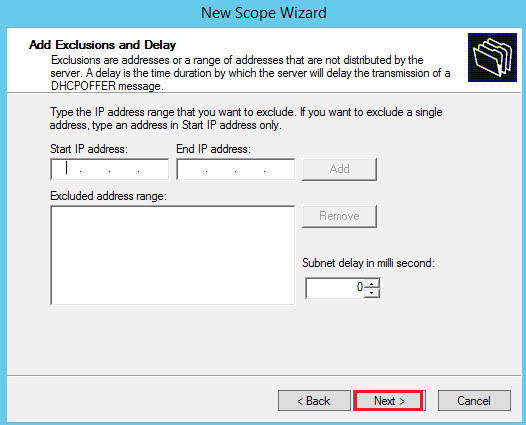
You can add exclusions to the range of IPs:
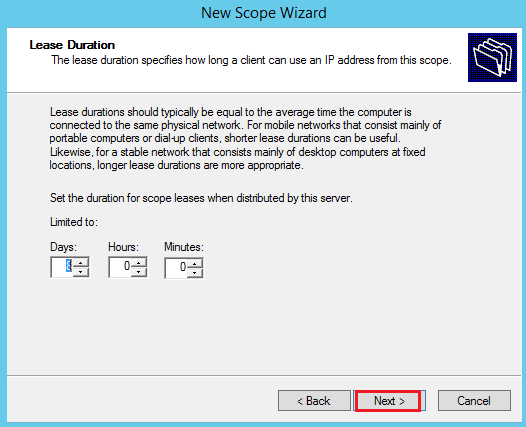
Default lease duration settings are fine:
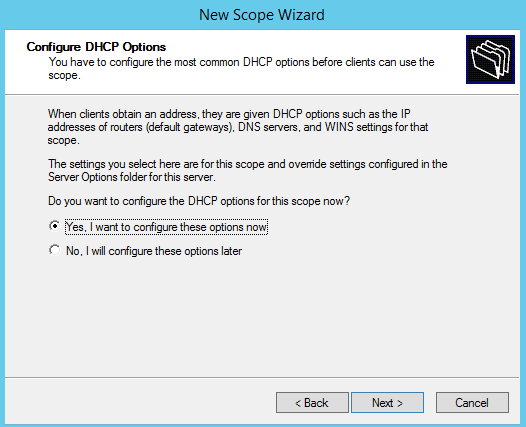
Choose Yes:
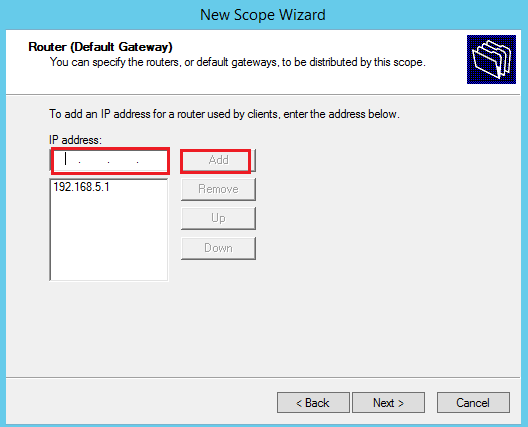
Add the gateway IP address:
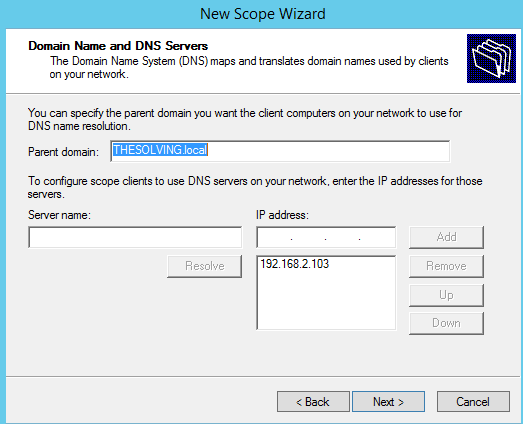
Specify the DNS servers:
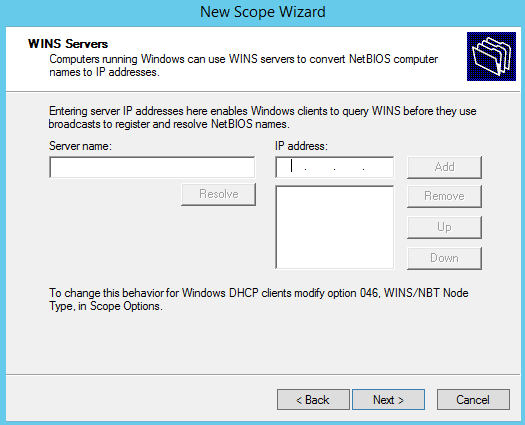
You don’t need to specify a WINS server:
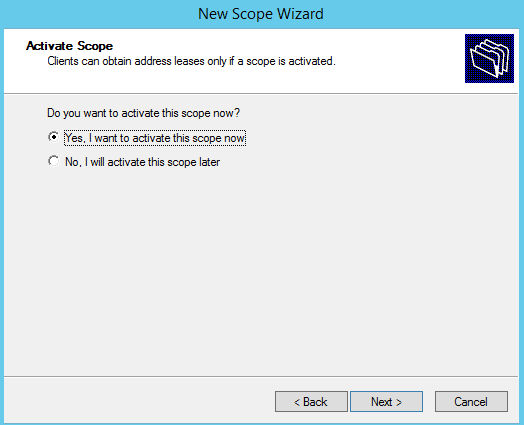
Choose Yes:
You’re ready to go!
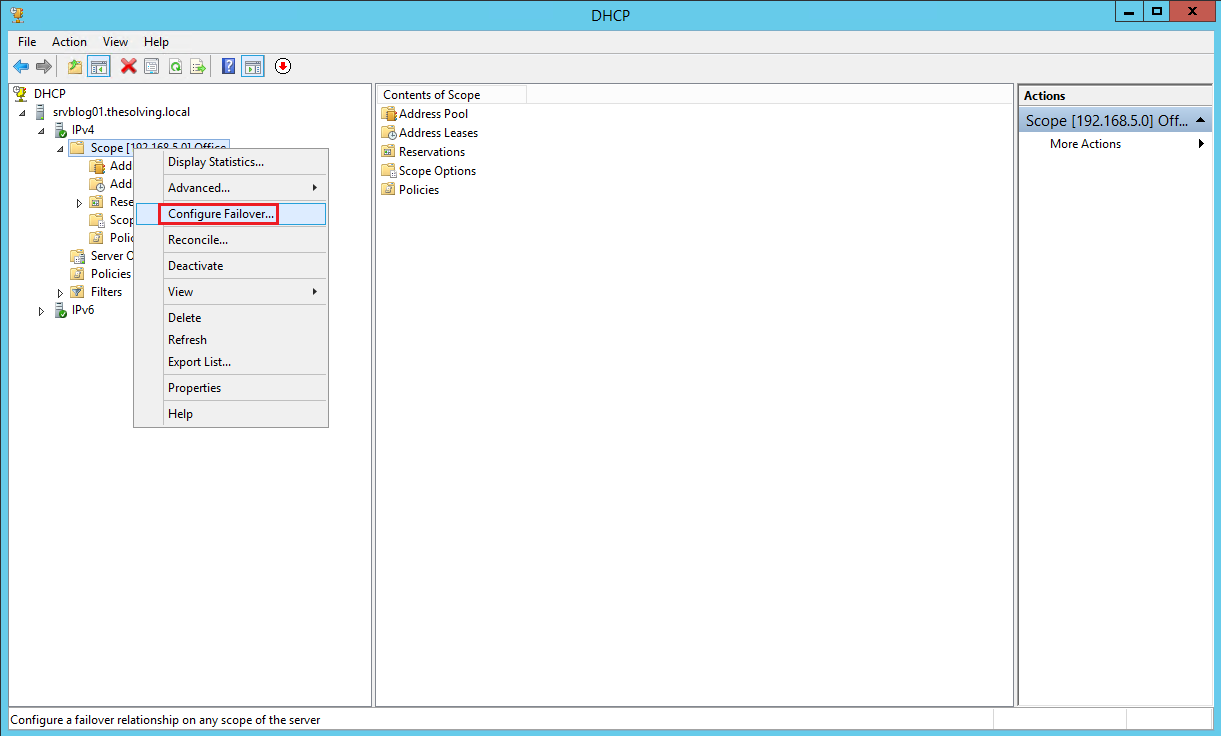
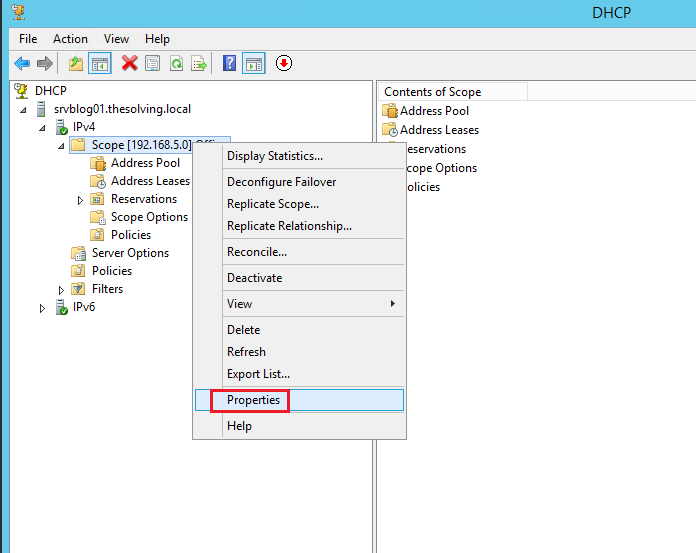
Right-click on Scope from the left column and select Configure Failover:
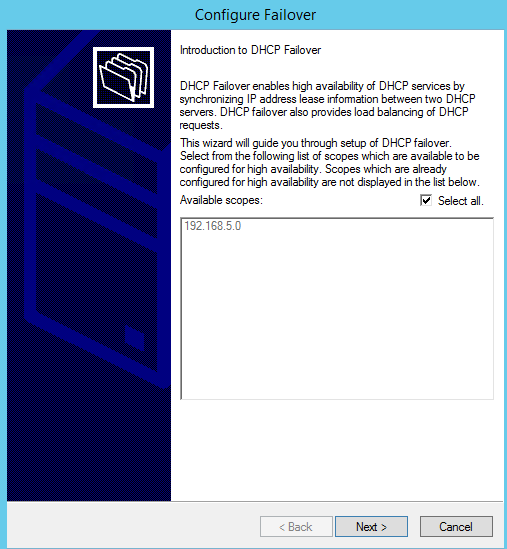
Check Select all:
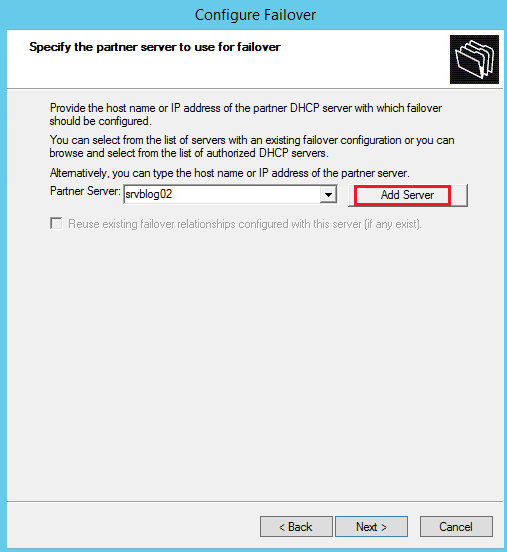
Click Add Server to add the partner server:
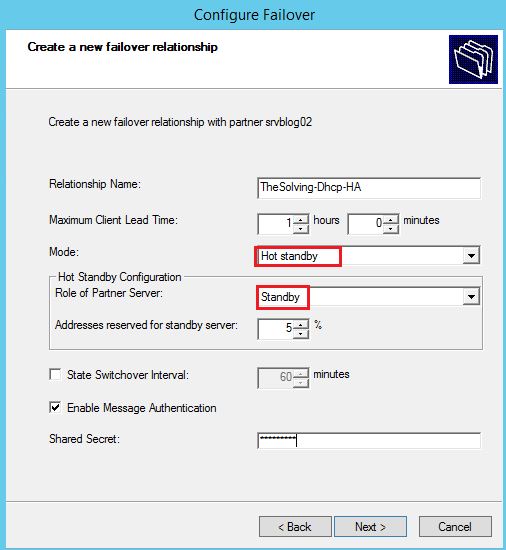
Select the failover mode, then specify the role of partner server (in our example Hot standby mode):
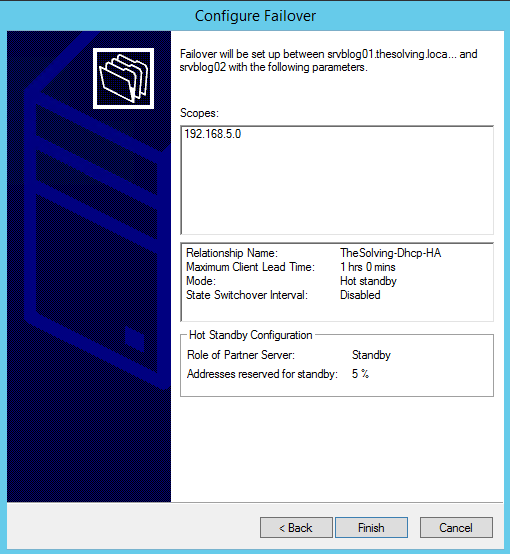
Click Finish:
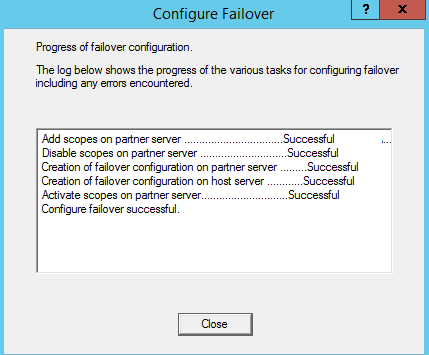
Check if all the jobs are completed successfully:
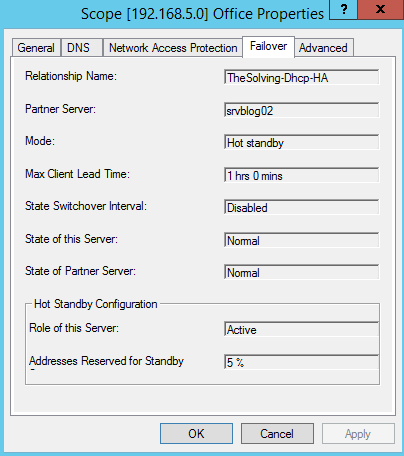
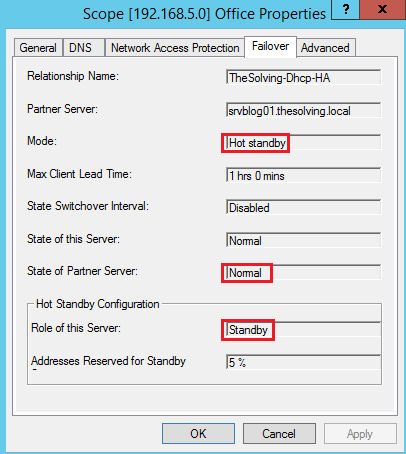
Right-click on Scope on the left column and select Properties, then open Failover tab:
Review the failover configuration status:
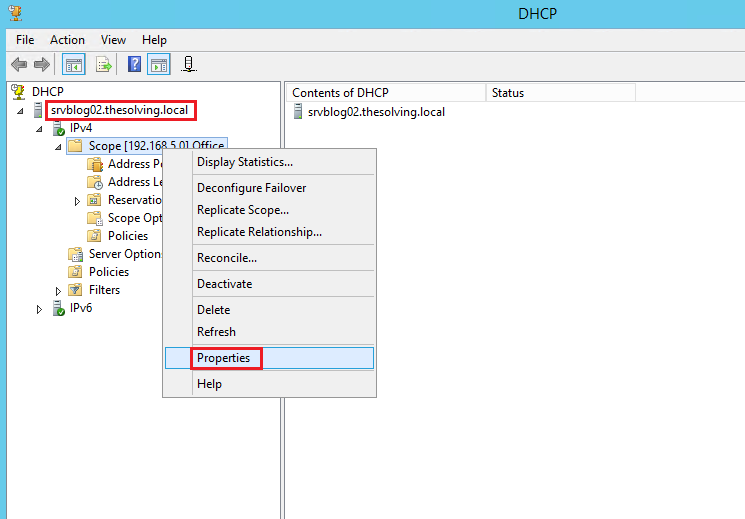
Repeat the operation on the partner server:
Review the failover configuration status of the partner server
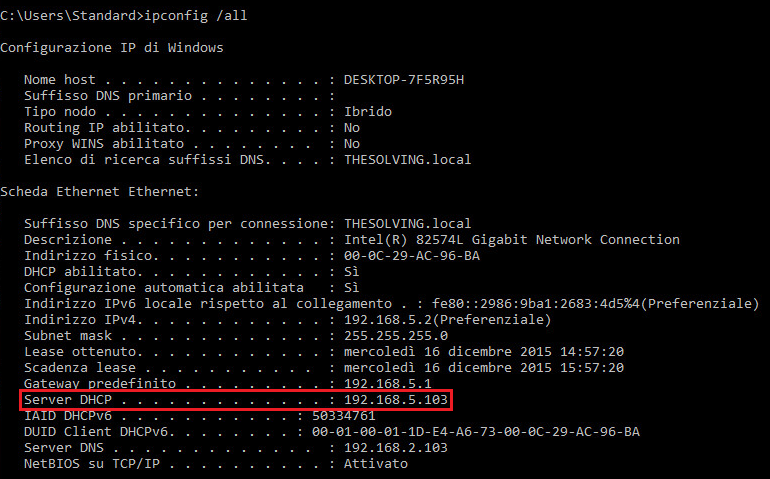
You’re ready to test the Hot standby failover! Set the PCs of the LAN to obtain the IP address through the DHCP Server (in our example the master server is 192.168.5.103):
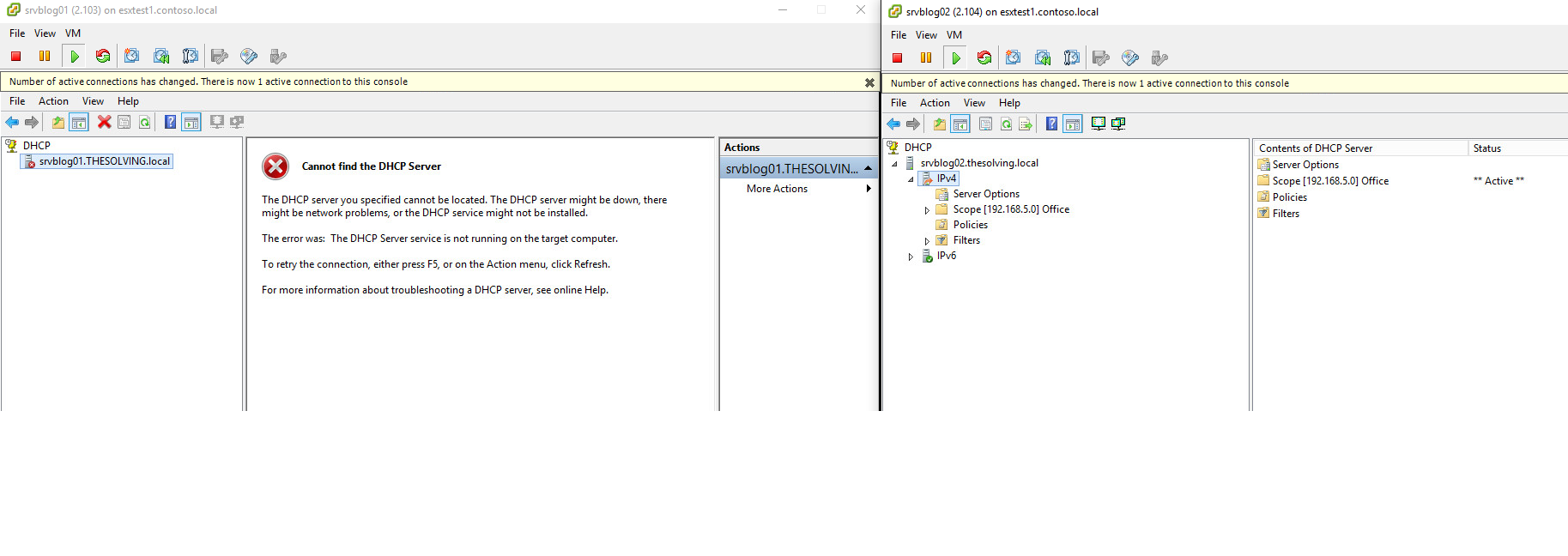
Stop the DHCP service on the Master server:
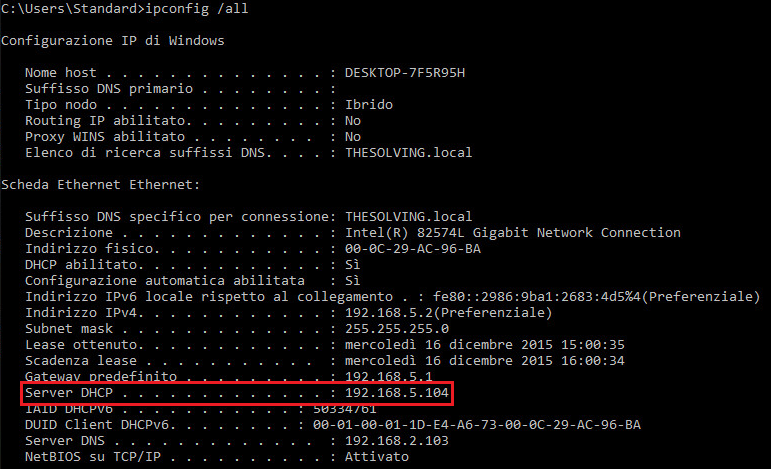
From the Windows prompt send the ipconfig /release command and then ipconfig /renew, if the failover works fine the IP address will be assigned by the server partner (in our example 192.168.5.104):
Read related articles
A Guide to PowerShell – part 3
Welcome to part 3 of 3 of The Solving A guide to PowerShell. Check also Part 1 and Part 2.
A Guide to PowerShell – part 2
Welcome to part 2 of 3 of The Solving A guide to PowerShell. Click here for Part 1 and Part
A Guide to PowerShell – part 1
Welcome to part 1 of 3 of The Solving A guide to PowerShell. Click here for Part 2 and Part

 Italiano
Italiano
 Español
Español