Storage Spaces is a storage virtualization technology developed by Microsoft and introduced with Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. It allows to create and manage logical volumes running on a pool of physical disks.
Storage Spaces supports redundancy and offers greater flexibility compared to a RAID setup.
Furthermore, creating a Storage Space is really quick and easy.
Open the Control Panel and click on the Storage Spaces icon or use the Windows search:
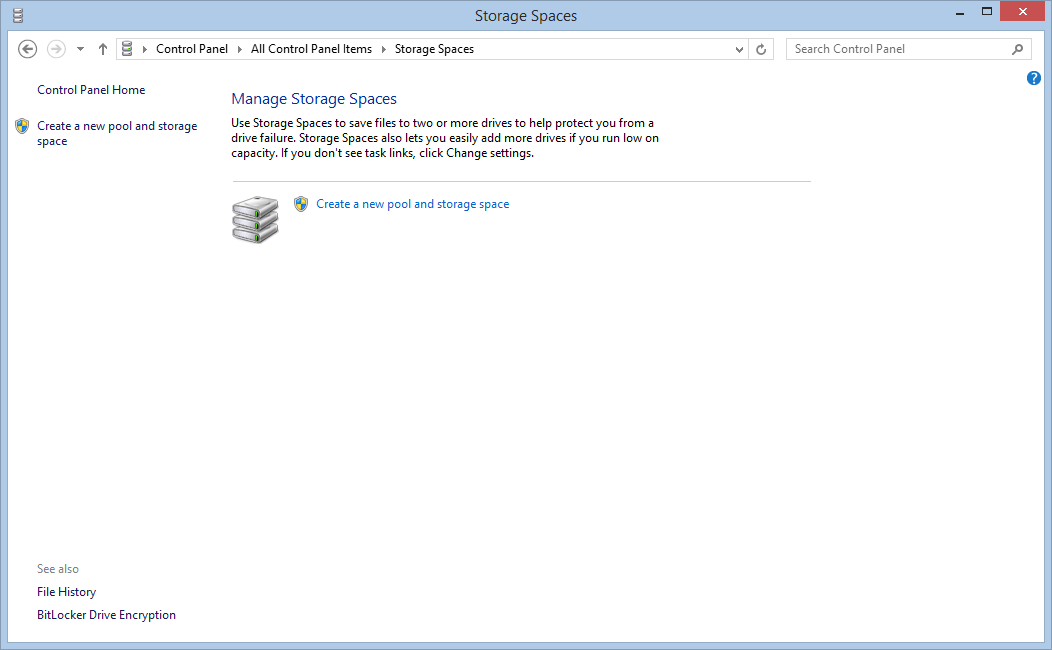
Click on Create a new pool and storage space:
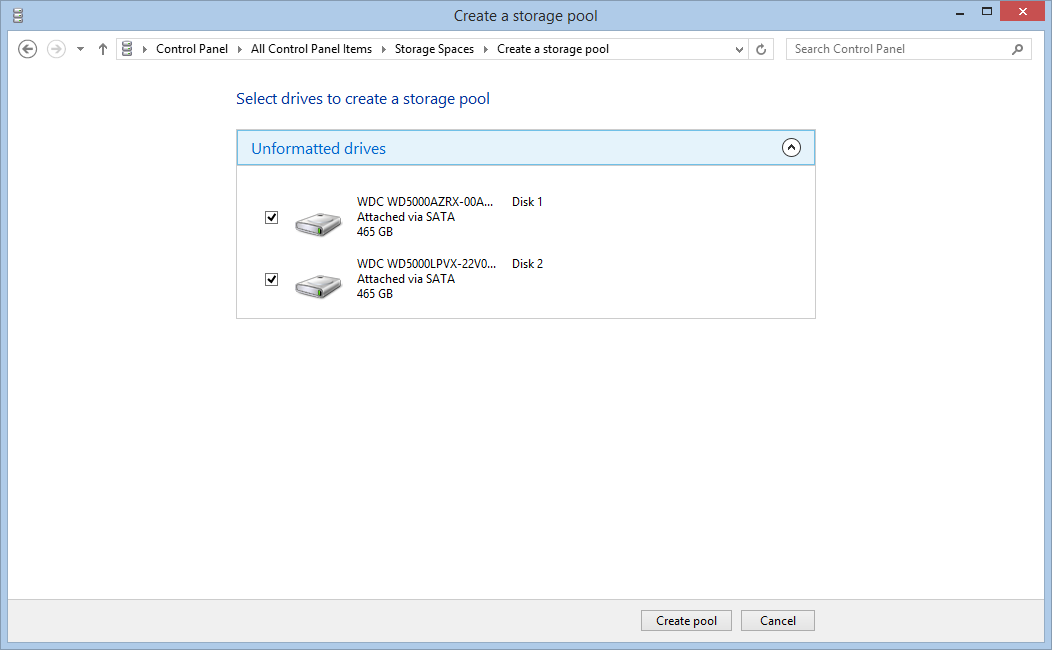
Select the drives:
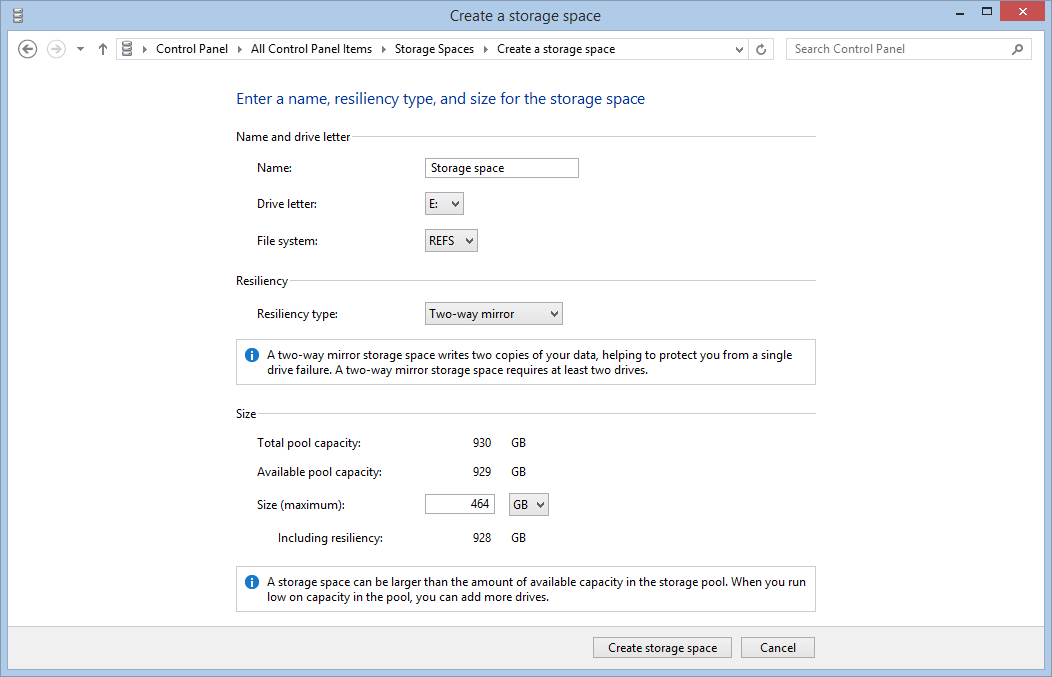
Choose the file system, we suggest ReFS for data storage, archives and to store digital disks of Hyper-V virtual machines – more information about ReFS here.
Then select the redundancy mode, we created a pool of two disks so we can only select Two-way mirror or use no redundancy. With three disks or more we suggest to use the Parity mode:
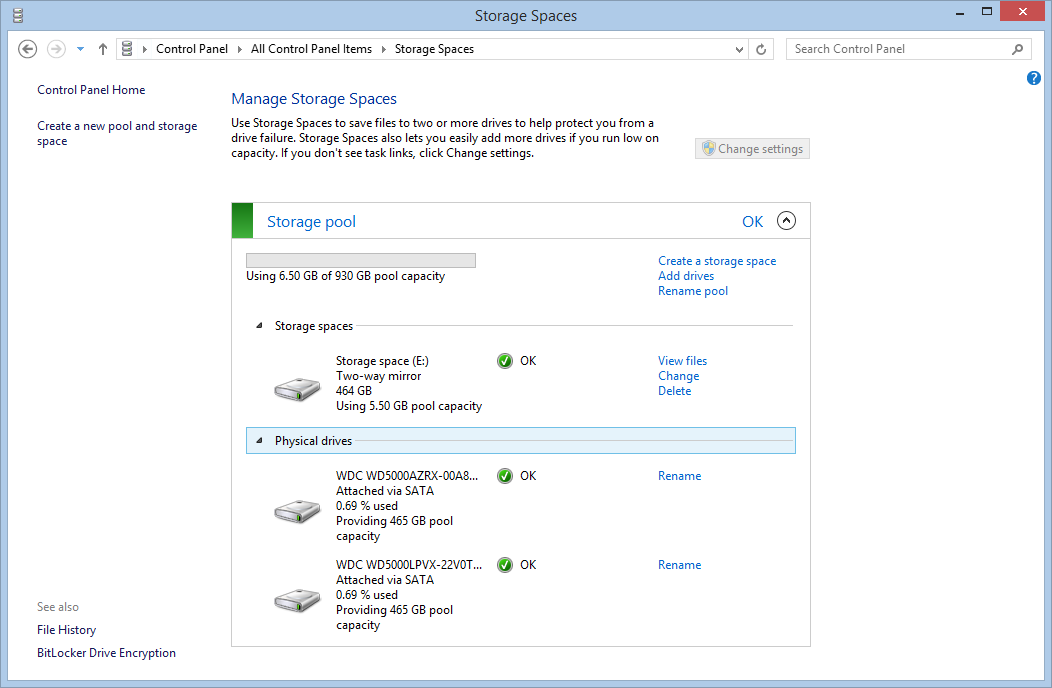
Now your Storage Space is ready. You can see the new volume in your Computer folder. You can expand the Storage Space in the future or delete it. In order to unlock the drives you need to delete the Storage Space and remove the physical units from the pool:
Read related articles
How to configure a Distributed File System (DFS) Namespace
Locating shared folders to access specific documents is a common problem in business environments. System administrators have to decide how
Configuring Volume Shadow Copies (VSS) on Windows Server 2012 R2
Volume Shadows Copies (also known as Volume Snapshot Service or VSS) is a technology developed by Microsoft to take restorable
Configuring NTFS quotas to set storage limits for users
Storage quotas help administrators to manage shared volumes. Windows Server 2012 // R2 supports a simple way to enforce quotas,

 Italiano
Italiano
 Español
Español