VMware vSphere is a very flexible platform, making you able to manage a group of virtual machines and resource pools in a single entity named vApp.
Let’s think about a web application running on a VM. The application also needs a database and other resources running on differente virtual machines. From a service point of view, all the virtual machines are part of the same entity and that’s why vApp exists.
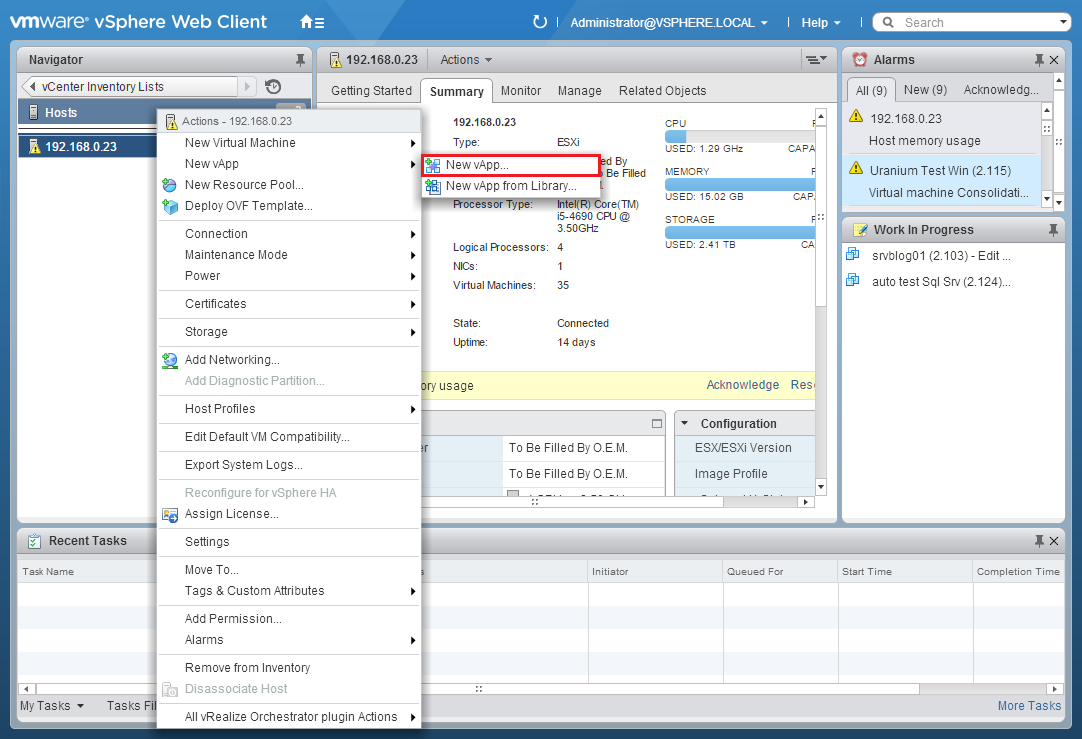
Configuring a vApp is simple. Access your vSphere Web Client and select the Host or the Cluster where the vApp will run. Right-click and select New vApp:
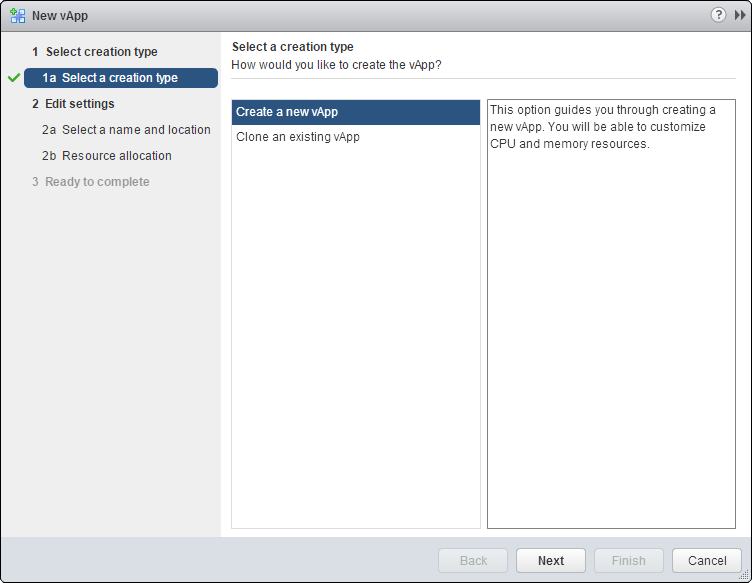
A wizard will start. Click Next:
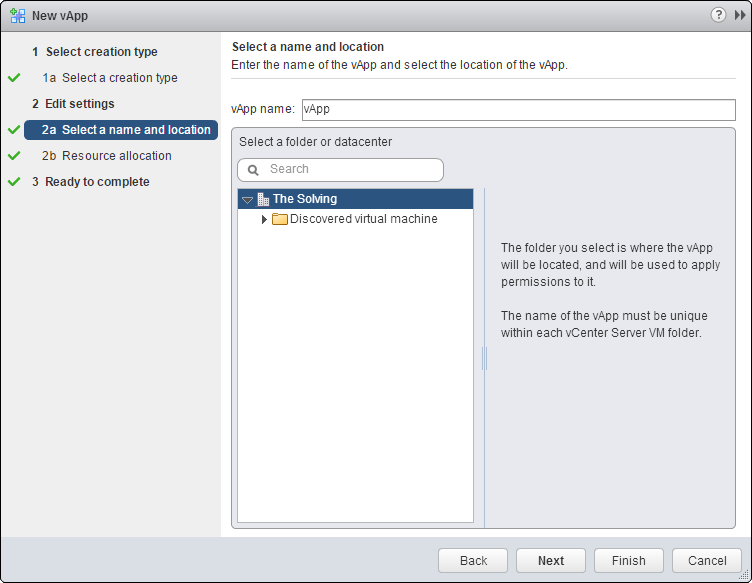
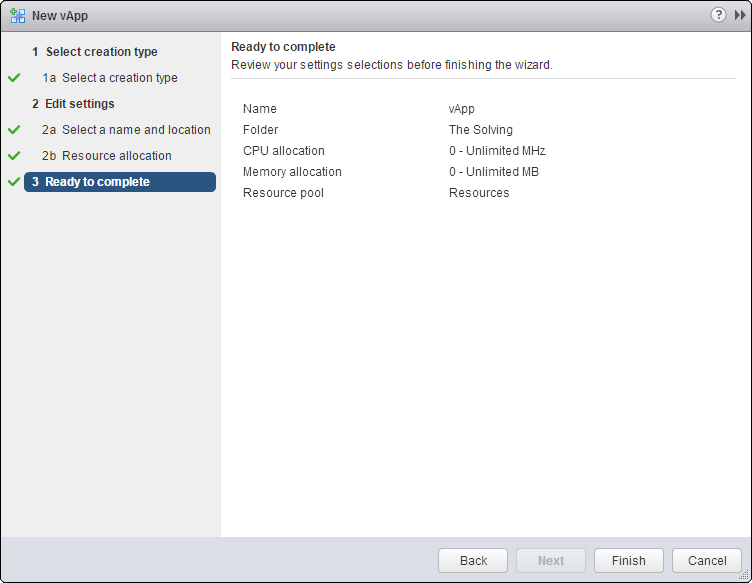
Name the vApp:
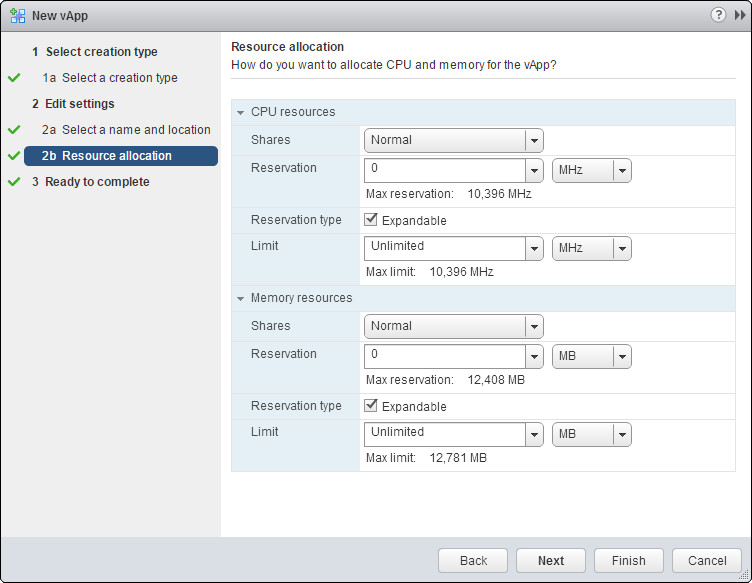
You can allocate resources dedicated to the vApp if you wish:
Click Finish and the vApp will be created:
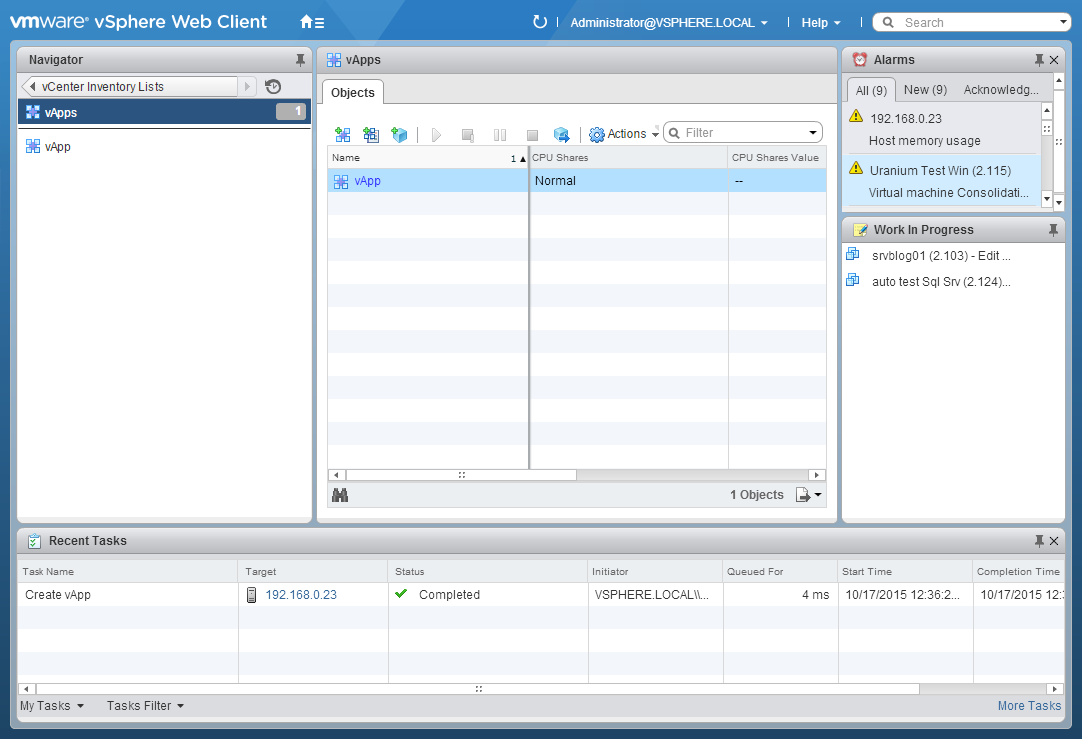
You will fine the new vApp in your Inventory, under the vApp area:
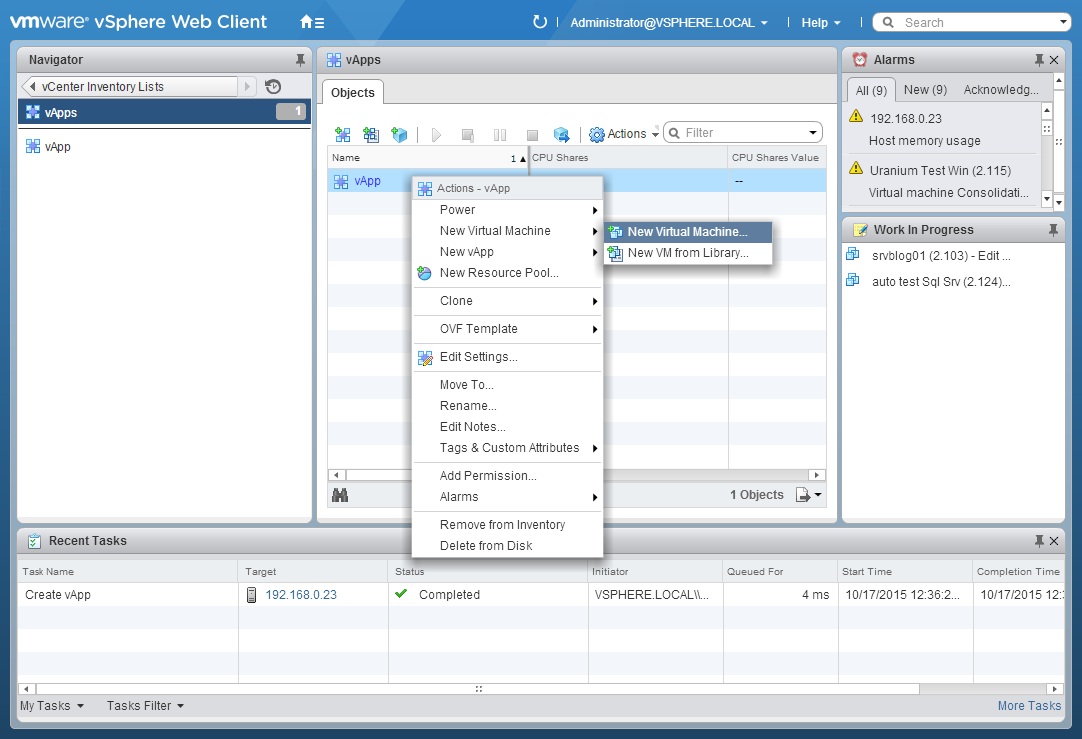
The vApp now is an empty box, we need to add the pieces required to make it works. For the most, you need to add virtual machines and it’s a pretty easy operation to perform. Right-click on the vApp and select New Virtual Machine:
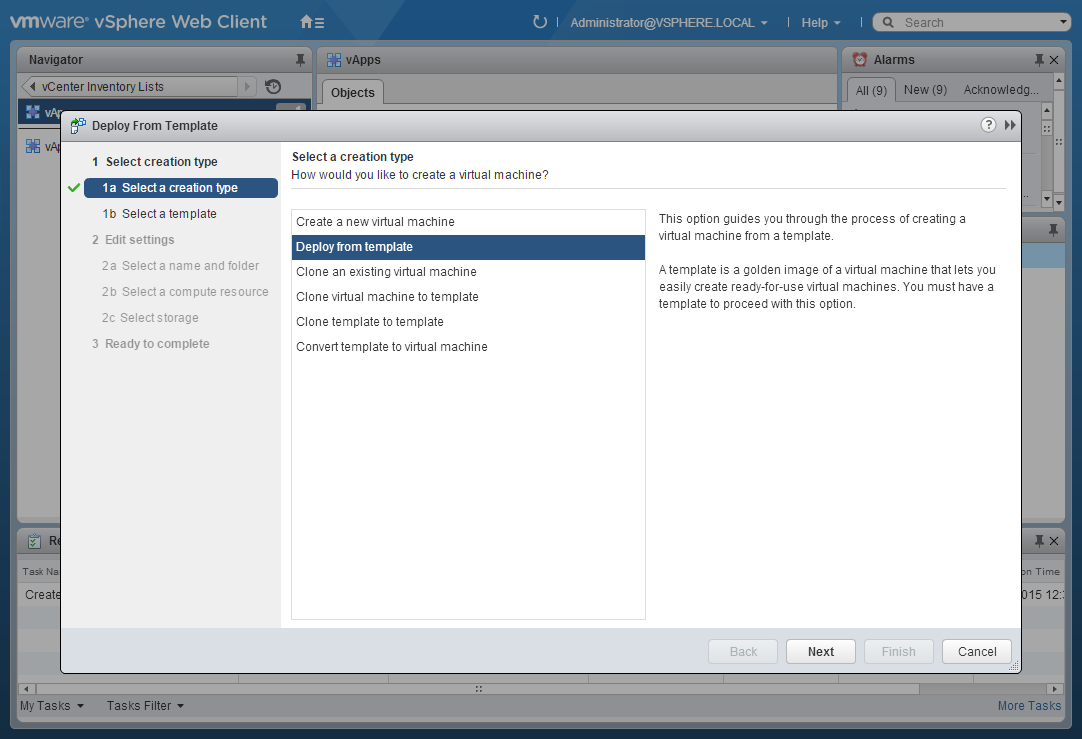
Another wizard will start. Add the virtual machines to the vApp:
Build your vApp and power it on.
Read related articles
Install VMware ESXi on a Hyper-V
It is possible to use nested virtualization to run VMware ESXi as a Virtual Machine in Hyper-V. To some, this
How to install and configure VMware PowerCLI version 10
VMware PowerCLI is a collection of Windows Powershell modules which are used to manage and maintain a VMware virtual environment.
How to set up a Hyper-V failover cluster
Hyper-V can enable high-availability using Windows Server Failover Cluster Manager. This allows you to create a virtual infrastructure which is

 Italiano
Italiano
 Español
Español