The VMware vCenter comes with several privileges grouped in Roles by default. The privileges and Roles allow the administrator to configure a granular security policy defining individual user rights.
On the vCenter there are three system roles as follows:
- No Access
- Read-Only
- Administrator
The system roles are permanent. there is no way to modify them. The No Access and Read-Only roles are very useful for restricting user access quickly.
The six default role samples are as follows:
- Virtual Machine Power User
- Virtual Machine User
- Resource Pool Administrator
- VMware Consolidated Backup User
- Datastore Consumer
- Network Administrator
While it is possible use the default sample roles as they are, it’s also possible to use them as a starting point to create custom roles. It’s considered a best pratice not to modify the default roles because they can be useful for future reference.
Now let’s create a custom Role.
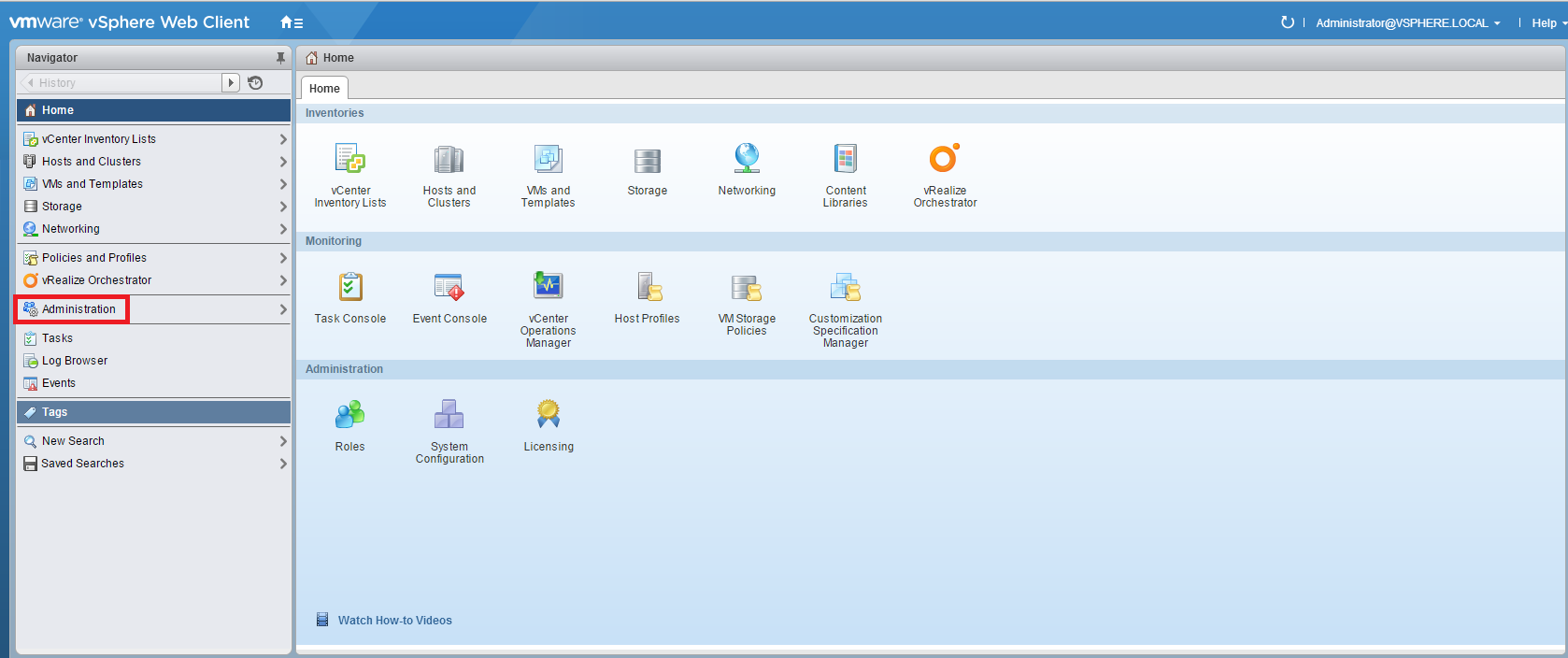
Log in your vSphere Web Client and click Administration:
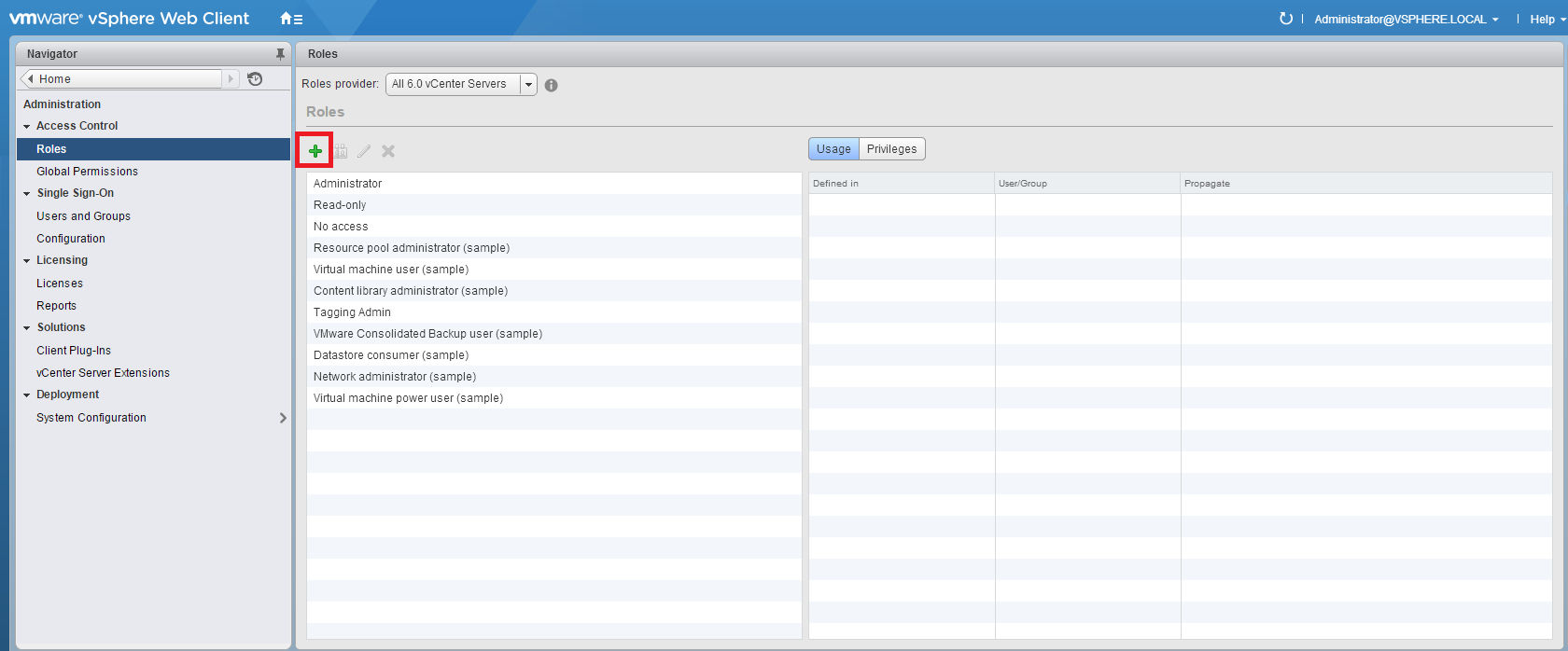
Select Roles and press +:
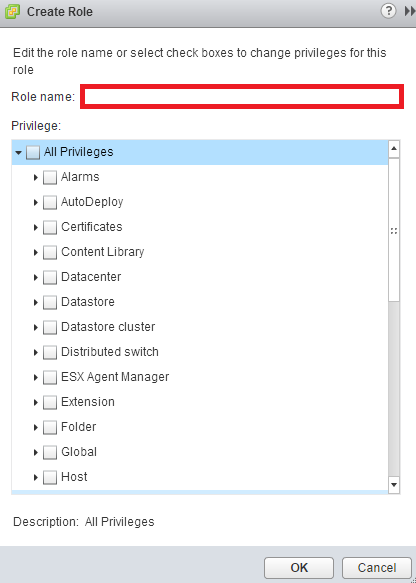
As you can see, a window will open allowing to define the name of new Role:
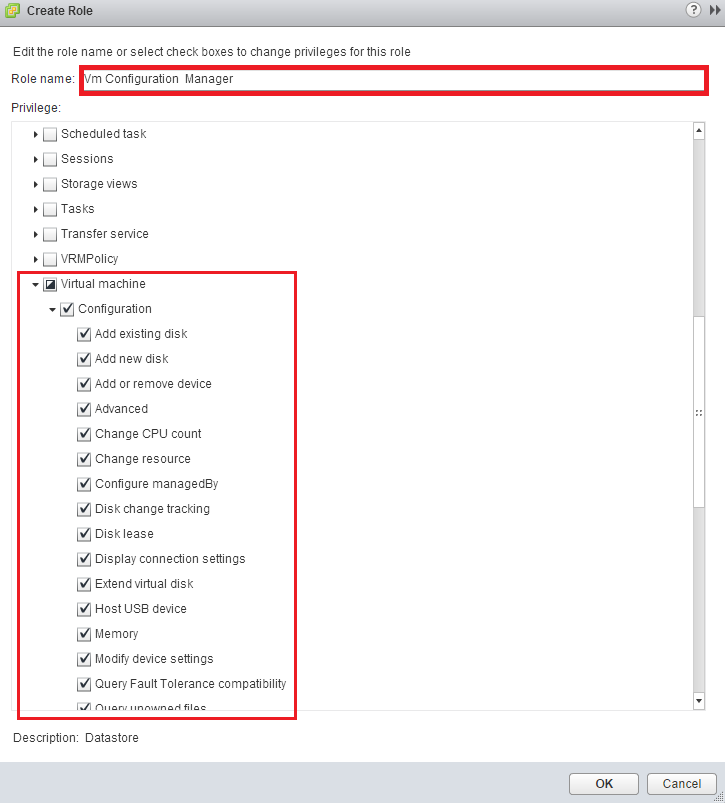
Name the new role (in our example we used: Vm Configuration Manager). Now scroll down to the Virtual machine privileges and check Configuration:
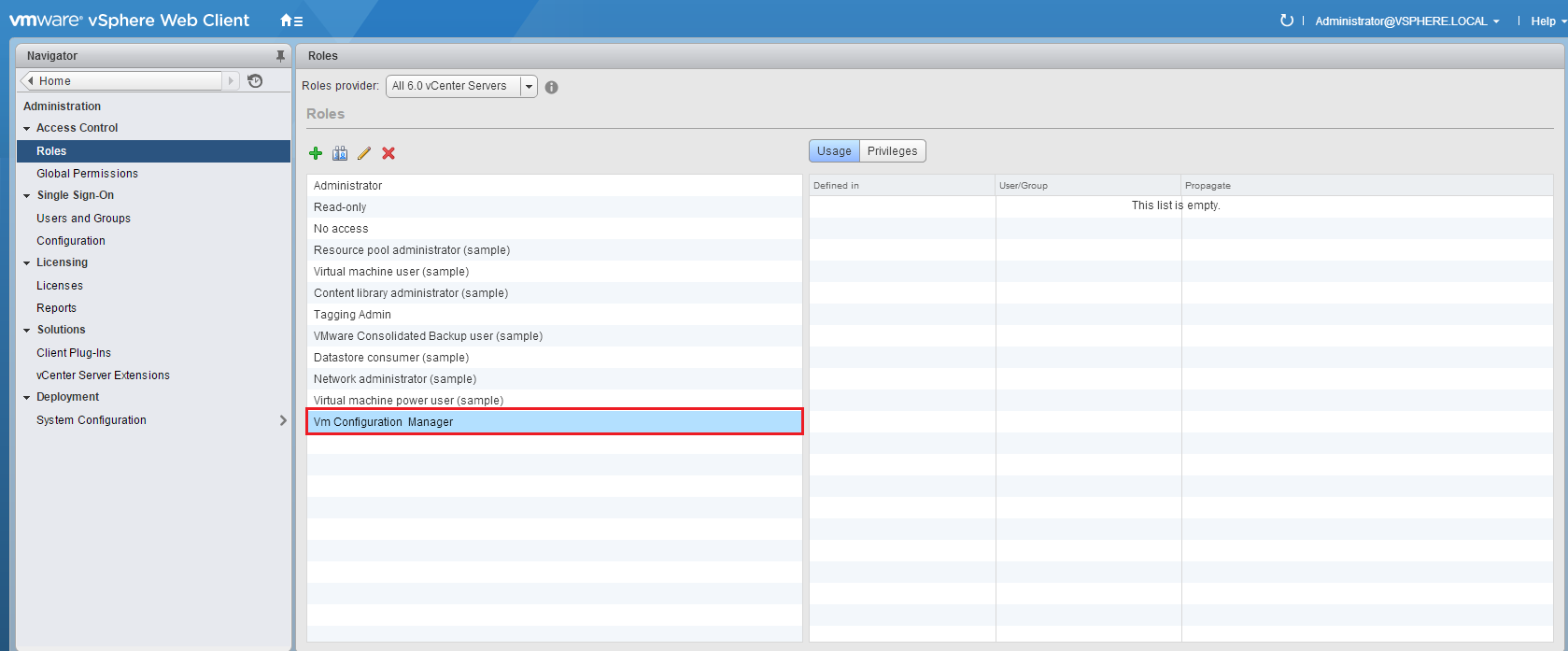
Review the list of the vCenter Roles, verify that the presence of the new Role:
Read related articles
Install VMware ESXi on a Hyper-V
It is possible to use nested virtualization to run VMware ESXi as a Virtual Machine in Hyper-V. To some, this
How to install and configure VMware PowerCLI version 10
VMware PowerCLI is a collection of Windows Powershell modules which are used to manage and maintain a VMware virtual environment.
How to set up a Hyper-V failover cluster
Hyper-V can enable high-availability using Windows Server Failover Cluster Manager. This allows you to create a virtual infrastructure which is

 Italiano
Italiano
 Español
Español